Intestinal parasitic worms are those simple organisms mostly present primarily on the intestinal wall in the gastrointestinal tract and suck liquid from the humans’ or animals’ body to live. Let’s discuss some common types of intestinal worms’ infections we can observe –
Jump to
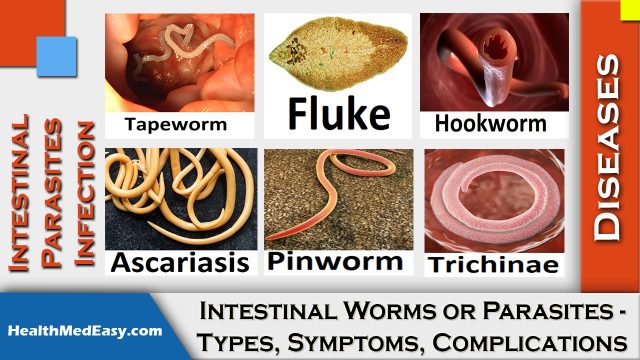
Tapeworms
A tapeworm, type of flatworm, is a white-colored worm generally lives and attaches itself to the intestinal wall. Most people with tapeworm infection experience either no symptoms or very mild symptoms. As the name suggests tapeworms are flat and are very long up to 50 feet depending upon its category. It also long lived in nature can live in our intestine for up to 30 years.
We can classify basically two types of tapeworm depending on where they generally live. Water-based tapeworms infected whenever we drink some uncleaned water this type of tapeworm entered into our body and when we eat some beef, pork, ingesting unclean or raw meats then meat-based tapeworms get into our body and infects the intestine.
Fluke Worms
A Fluke, another type of flatworm, are small in size and have a rounded leaf shape generally takes shelter in the tissues, blood, or intestines. It very often causes infection in animals but can also affect humans when accidentally eating or ingesting them, either through water-based plants, such as watercress or with drinking water.
Once flukes are entered into the body, adult flukes occupy the bile ducts and liver which may occur inflammation of the bile ducts or complete blockages. Generally, we cannot get any symptoms of this fluke infection but after some months or year later we may experience symptoms of abnormally large liver or unusual readings on a liver test.
Hookworms
Hookworm is a type of roundworm which is less than half an inch sized long. It lives in the small intestines and generally enters a person’s body through feces of infected living organisms and infected soil. They lay eggs in the intestine, a portion of those eggs also pass out through feces, larvae came out from those eggs. Thus more people get infected when larvae get into our body through the skin. Hookworm is named as one end of its body tapers off into a needle or hook shape.
According to the CDC estimation, approx 576 to 740 million people in the world have an infection by hookworms. Most of the time hookworm infection shows no symptoms. But some people may be troubled with typical gastrointestinal symptoms which is very common with first-time infections.
Ascariasis Worms
Similar to hookworm, ascariasis is also a type of roundworm but longer that hookworm. They are generally a few inches long, lives in intestines, lay eggs which contaminates soil after pass out through feces. People can get infected when they ingest their eggs with infected foods.
Ascariasis generally does not show any major symptoms at the primary stage but severe infections, intestinal blockages, impaired growth of children can be possible.
Pinworm (Threadworm)
A pinworm or threadworm is a type of roundworm, generally thin and small in size like the size of a staple, found mostly in children. Pinworms are generally live in the colon and rectum of infected humans and are considered less harmful than any other type of parasitic worms.
Pinworm infection takes place when someone makes a direct contact or use the contaminated things shared with infected individuals. Generally, symptoms are mild and may not be seen other than itching-like symptoms found on the skin around of anus when female pinworms crawl out of the anus to lay their eggs which sometimes makes the sleep difficult.
Trichinae Worms
Trichinosis worm, a parasitic nematode worm, is another type of roundworm cause infection in humans and other mammals. Though this infection is generally rare in the US, individual get infected after they eat contaminated uncooked or raw wild meats, such as seal meats, pork, bear etc. These larvae covered with a hard cyst which protects it until transferred to another host. While growth trichinae mostly live in the small intestine but after full-grown, it changes its location to other tissues (e.g. muscles).
Trichinae infection shows various symptoms varying from common gastrointestinal symptoms to severe health issues like muscle aches, chills, swelling of the face or eyes, joint pain etc. If there are heavy infections then movement, breathing or heart problems even death may occur.